Chopping Board Colours: Your Complete Guide



Chopping Board Colours: Your Complete Guide
Visit any commercial kitchen or catering equipment store and you’ll see a rainbow of chopping boards. But what do the different colours mean? In this article, our experts explain how the colours of chopping boards help reduce the risk of cross-contamination and what each colour is used for.
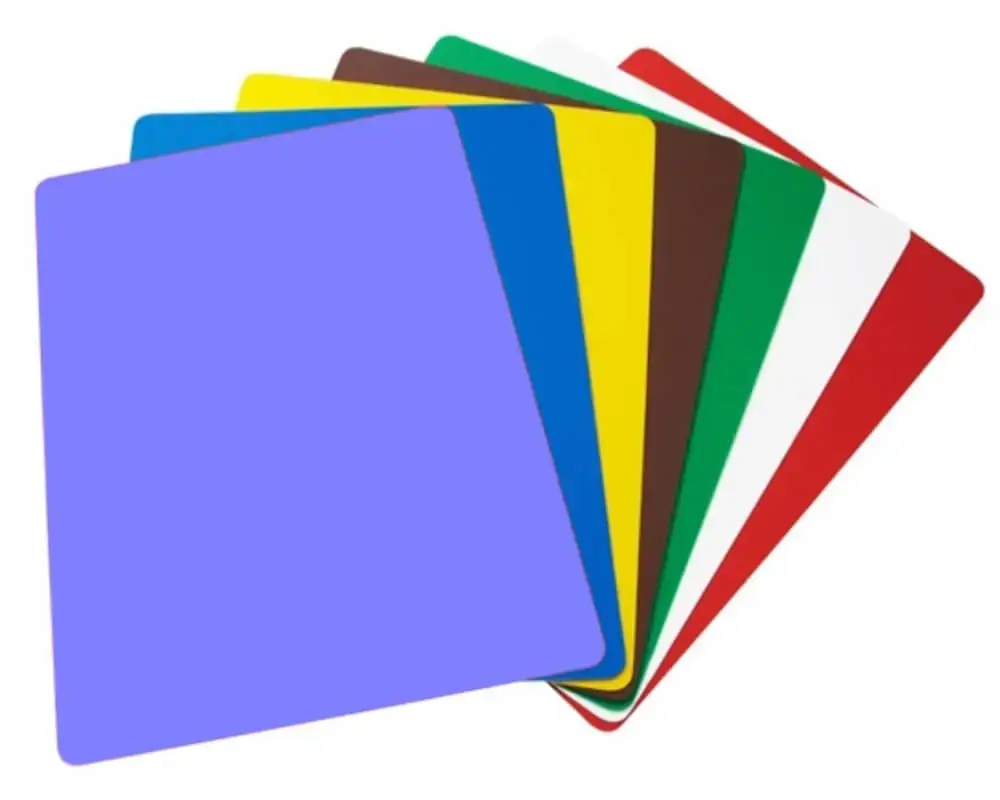
What do the different chopping board colours mean? We’ve outlined the chopping board colour standard below:
|
Food Item |
Colour |
|
Raw Meat & Poultry |
Red |
|
Raw Fish |
Blue |
|
Cooked Meat & Fish |
Yellow |
|
Washed Fruit & Vegetables |
Green |
|
Unwashed Vegetables |
Brown |
|
Dairy & Bakery Items |
White |
|
Anti-Allergen Foods |
Purple |
Commercial kitchens employ a system of colour-coded chopping boards to effectively prevent cross-contamination and uphold food safety standards. Each colour is specifically designated for particular food groups, allowing kitchen staff to quickly and easily identify the appropriate board for different types of food. For instance, a red board is typically reserved for raw meats, while a blue board might be used for fish, and a green board is generally designated for fruits and vegetables. This systematic approach not only streamlines food preparation but also significantly reduces the risk of transferring harmful bacteria and allergens between food items. By implementing this colour-coding system, kitchens can maintain a higher level of hygiene and safety, ultimately protecting the health of consumers and the integrity of the culinary environment.
The colour of the chopping board indicates the type of food product (or group) being prepared on it. Not only does this act as a cue for visual communication, but it also helps reduce the risk of cross-contamination within a kitchen. Colour-coded boards fall within ‘The Four Cs’ of food hygiene, which you can learn more about in one of our recent blogs - ‘What Are The Basic Food Hygiene Rules?’
There is the option to use a different colour-coded system, provided that this is outlined in detail in your Food Safety Management System, and your staff are made aware of the deviation from the standard. Most kitchens, however, use the same universal guidelines, which we’ve outlined below:
Raw Meat & Poultry
The red chopping board is used for raw meats, including chicken, beef, pork, turkey, pheasant, and other meats from the same family. By keeping raw meat separate, you’ll reduce the risk of spreading Salmonella or E-Coli to ready-to-eat foods.
Because some meat can be eaten raw (such as beef), you must avoid cross-contamination from meats that are not safe to eat raw. To do so, you must wash your chopping board between preparing different types of meat.
Raw Rish (Including Shellfish)
Blue chopping boards are used to prepare fish that is about to be cooked. Raw fish includes fin and shellfish, as well as prawns, shrimp, muscles, clams, oysters, salmon, cod, and more.
The reason that raw fish is prepared on a separate chopping board from raw meat is that they each hold different bacteria and therefore pose different threats to one another. The same applies to the types of fish you are preparing, which is why you should wash or change your board between preparing different kinds of fish.
Cooked Meat, Poultry, & Fish
The yellow chopping boards can be used for cooked meat, poultry and fish. Interestingly, fish that is going to be served raw, such as fish found in sushi and sashimi, is safe to prepare on a yellow chopping board as it is classified as ‘ready to eat’. In this scenario, some sushi chefs prefer to use a black chopping board.
Washed Vegetables & Fruit
The green and brown boards are often confused due to their similarities in use. The green chopping board is most commonly used for fruits and salad vegetables, such as lettuce, cucumber, and tomatoes. Other vegetables can be chopped on a green board providing that they have been washed thoroughly (this is particularly important for root vegetables that contain traces of soil).
Unwashed Vegetables
The brown board is generally used to prepare unwashed vegetables, typically those of the root variety, such as carrots, parsnips, potatoes, and beetroot. Please note that not all vegetables can be washed properly, such as mushrooms (because they just soak up water), and therefore, they should always be prepared on a brown chopping board.
If you’ve washed your root vegetables properly, by scrubbing them under warm running water, they can then be safely chopped on a green chopping board.
Dairy Products & Bakery Items
The white chopping board is typically used for dairy products, such as cheese or butter, as well as for everyday bakery products, including bread, cakes, pastry, and pizza. It’s very common for people to be allergic to dairy products, so it's essential to take extra care to wash the board thoroughly between uses.
Anti-Allergen Foods (Such As Gluten-Free Bread)
Whilst the purple chopping board isn’t usually included in coloured sets, it is an important addition to any kitchen. Use the purple chopping board to prepare anti-allergen foods or ‘free from’ products, such as gluten-free bread. Some kitchens may use the purple board to keep allergen foods separate; for example, to chop nuts on rather than using the green chopping board.
Using Your Chopping Boards Safely
Without a combination of safe practices in your kitchen, colour coding your boards won’t eliminate all the risks of cross-contamination. Below, we outline a few rules to follow to maintain a high standard of food hygiene with chopping boards in your kitchen:
Clean Between Uses
Clean and disinfect your chopping boards (and knives) between uses, even if you are preparing ingredients that fall within the same food group. This helps to avoid contamination and reduces the risk of spreading allergens.
It is an important step that many don’t consider. For example, some beef may be safe to serve raw. However, if you have just used the red chopping board to prepare raw chicken, you may contaminate the beef, making it unsafe to eat.
Colour-Coded Knives
Not only should your chopping boards follow a colour-coding system, but the accompanying knives should also be colour-coded based on the item that they are chopping. This, like the boards, offers a visual cue to staff in the kitchen, ensuring that knives aren’t carrying bacteria from one food group to another.
Swap Your Boards
You must ensure that no chopping board is used for more than a few hours at a time, even when preparing the same type of food. This increases the risk of bacterial growth, a significant concern in warm kitchen environments. Ensure you have multiples of the same coloured chopping boards and swap them out regularly, at least every hour.
We cover many of these topics in-depth in our online Food Hygiene course. If you’d like to learn more about the certification and its benefits, why not read one of our recent blogs - ‘How Long Does a Food Hygiene Certificate Last?’
Both hardwood and plastic are great options for chopping boards. However, plastic sits at the top of our list for several reasons:
- easier to keep dry;
- generally more cost-effective when compared to high-quality wooden boards;
- reduced risk of cracks developing, which harbour bacteria;
- can be cleaned in a dishwasher at a high temperature.
Are Wooden Chopping Boards Hygienic?
Yes and no. It is a common misconception that wooden chopping boards are unhygienic due to their porous surface and that wood is harder to clean. However, this claim was falsely made by the U.S. Department of Agriculture several years ago and has since been debunked. Some woods, such as Maple, Bamboo, or Teak, have antibacterial properties that can resist or even kill bacteria.
The reason we deem wooden chopping boards to be unsafe is due to the lack of colour variations, or rather, the colour itself. The colour-coded chopping board system is in place to reduce the risk of cross-contamination, serving as a visual cue for effective communication. If you use wooden chopping boards, you won’t be able to identify what the board has been previously used for.
The answer is not a question of time but rather the condition of your chopping boards. If your boards no longer sit flat on the surface, they should be replaced. Bent or warped chopping boards may mean they don’t grip your surface and are more likely to slip whilst you are chopping, increasing the risk of injury.
The most important indication that a board needs replacing is the number of knife grooves on its surface. These marks make the chopping board harder to clean and unknowingly trap bacteria.
HSE Docs is an approved supplier to the central government and the public sector, so you can trust our team to bring you comprehensive online training with certificates that are recognised UK-wide.
For as little as £4.99, you can get qualified at level 2 in Food Hygiene & Safety. The course, which can be completed in two hours, provides in-depth information on HACCP, risk assessments, temperature control, contamination risks, chopping board colours, and more, ensuring you meet the gold standard for kitchen health and safety.
If you’d like to learn more, don’t hesitate to reach out to our team. For more HSE certificate courses from HSE Docs, explore our ‘Online Courses’ page.

 CART
CART